Probability Questions and Answers

Math
ProbabilityWhat is the probability that a card drawn randomly from a standard deck of 52 cards is a six? Express your answer as a fraction in lowest terms or a decimal rounded to the nearest millionth.
Choose the correct answer from the options below.
1/4= 0.25
1/13≈ 0.076923
1/26≈ 0.038462
1/52≈ 0.019231

Math
ProbabilityThe Marvel Costume Design Workshop employs 65 people. Eight of the 30 men and 21 of the 35 women work in the business office. What is the probability that an employee picked at random is a woman or works in the business office?
A. 64/65
B. 21/65
C. 43/65
D. 10/13
E. 51/65

Math
ProbabilityFind the probability of the given event.
A bag contains 5 red marbles, 3 blue marbles, and 1 green marble. A randomly drawn marble is not blue.
A. 6
B. None of these
C. 1/2
D. 3/2
E. 1/3

Math
ProbabilityIn one state lottery game, you must select four digits (digits may be repeated). If your number matches exactly the four digits selected by the lottery commission, you win.
a) How many different numbers may be chosen?
b) If you purchase one lottery ticket, what is your chance of winning?
a) There are different numbers that can be chosen.
(Type a whole number.)
b) There is a chance of winning.
1 in 10,000
1 in 9999
1 in 6561
1 in 100
1 in 1000

Math
ProbabilityOne card is selected at random from a deck of cards. Determine the probability of selecting a card that is less than 7 or a diamond. Note that the ace is considered a
low card. The probability that the card selected is less than 7 or a diamond is
(Type an integer or a simplified fraction.)

Math
ProbabilityFind the indicated probability.
If P(A and B) = 0.5, P(A) = 0.7, and
P(B) = 0.6, find P(A or B).

Math
ProbabilityIn an auditorium with 500 people, one person will be chosen to win a $100 gift card. The rest of the people will receive a $0.25 key chain.
What is the probability that you will be chosen to win the gift card?
What is the probability that you will receive a key chain?
Find the expected value.

Math
ProbabilityA standard deck of cards contains 52 cards. One card is selected from the deck.
(a) Compute the probability of randomly selecting a two or ten.
(b) Compute the probability of randomly selecting a two or ten or ace.
(c) Compute the probability of randomly selecting a two or diamond.

Math
ProbabilityA binomial probability experiment is conducted with the given parameters. Compute the probability of x successes in the n independent trials of the experiment.
n=9, p=0.4, x≤ 3

Math
ProbabilityAn airline is planning its staffing needs for the next year. If a new route is approved, it will hire 811 new employees. If a new route is not granted, it will hire only 193 new employees. If the probability that a new route will be granted is 0.35, what is the expected number of new employees to be hired by the airline? The expected number of new employees to be hired is.

Math
ProbabilityAt the Royal Dragon Chinese restaurant, a slip in the fortune cookies indicates a dollar amount that will be subtracted from your total bill. A bag of 10 fortune cookies is given to you from which you will select one. If six fortune cookies contain "$1 off," three contain "$3 off," and one contains "$6 off," determine the expectation of a selection.

Math
ProbabilityFour million tickets are sold for a lottery.
a) If you purchase a ticket, find your odds against winning.
b) If you purchase 50 tickets, find your odds against winning
a) If you purchase a ticket, find your odds against winning.
b) If you purchase 50 tickets, find your odds against winning.

Math
ProbabilityDuring a game of online hearts, three cards are dealt, one at a time without replacement, from a shuffled, ordinary deck of cards.
Find these probabilities rounded to six decimal places:
(a) All are red cards.
The probability that the three cards dealt are all red cards is
(b) All are diamonds.
The probability that the three cards dealt are all diamonds is

Math
ProbabilityThe volume of water in swimming pools in a local neighborhood is normally distributed. What is the percentage of volumes that are within 3 standard deviations of the mean? Write your answer as a percent (use %) rounded to 1 decimal point.

Math
ProbabilityOn one large campus, 16% of students surveyed said that they spend less than an hour a night studying. If three students are chosen randomly, find the following probabilities.
(a) What's the probability that all three spend less than an hour a night studying? Express your answer as a decimal rounded to four decimal places.
The probability that all three spend less than an hour a night studying is 0.0041
(b) What's the probability that two of the three spend less than an hour studying? Express your answer as a decimal
rounded to four decimal places. Do not round any intermediate calculations.
The probability that two of the three spend less than an hour a night studying is

Math
ProbabilityYou throw a dart at the board shown. Your dart is equally likely to hit any point inside the square board.
a. What is the probability your dart lands in the smallest triangle?
b. What is the probability your dart does not land anywhere in the circle?

Math
ProbabilityThe length of human pregnancies varies normally with a mean of 266 days and a standard deviation of 16 days.
What percentage of pregnancies last longer than 282 days?
32%
68%
5%
16%

Math
ProbabilitySuppose Carolina Hurricane hockey player Martin Necas has an 18% chance of scoring every time he takes a shot at the goal. During one particular game, he gets 6 shots at the goal. Use the binomial distribution
to calculate the following probabilities.
a) Find the probability he makes exactly 1 goal.
b) Find the probability he makes at most 2 goals
c) Find the probability that he makes at least 4 goals.
Math
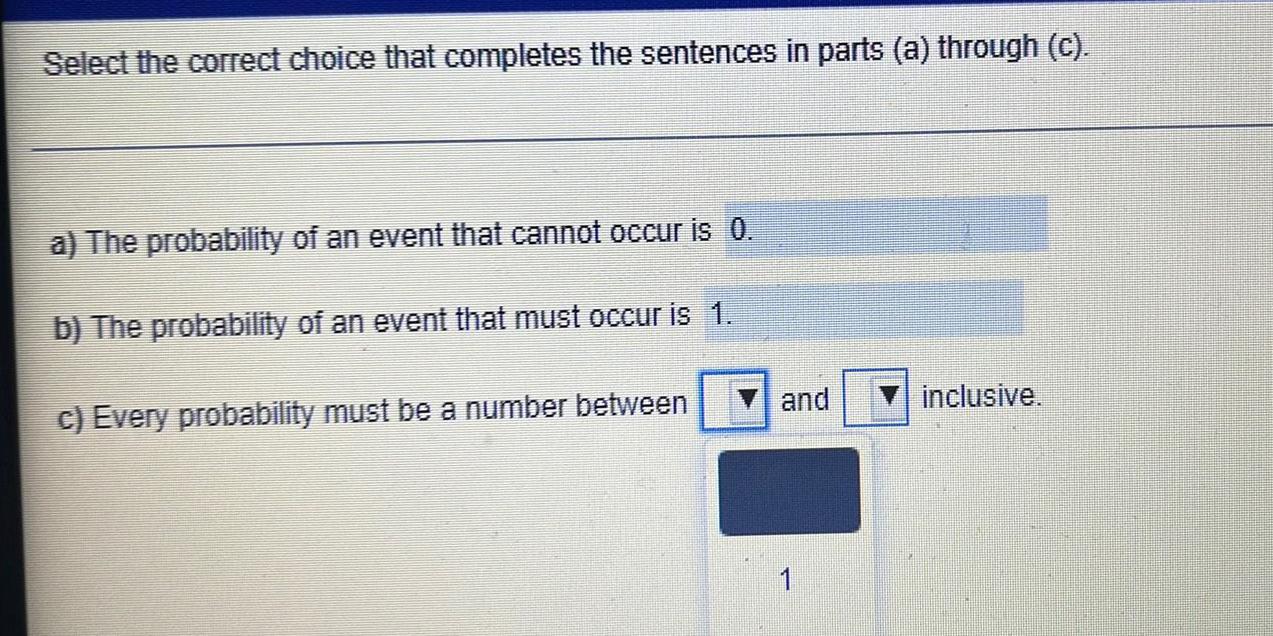
ProbabilitySelect the correct choice that completes the sentences in parts (a) through (c).
a) The probability of an event that cannot occur is 0.
b) The probability of an event that must occur is 1.
c) Every probability must be a number between
Math
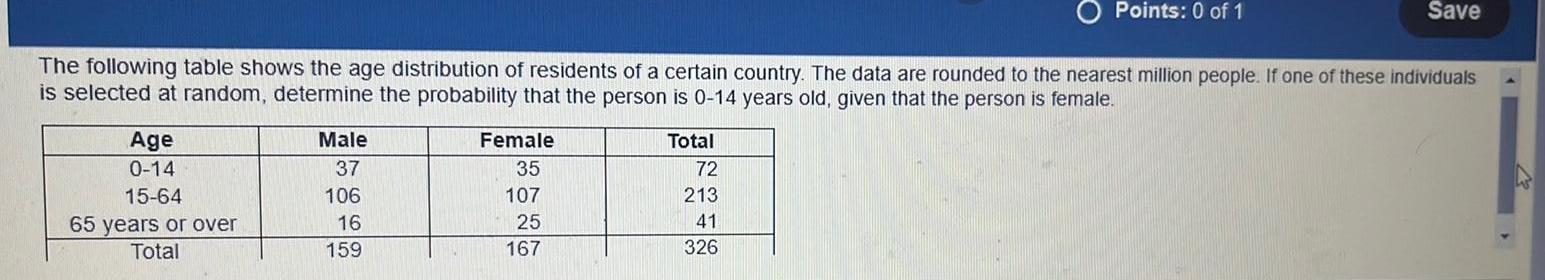
ProbabilityThe following table shows the age distribution of residents of a certain country. The data are rounded to the nearest million people. If one of these individuals is selected at random, determine the probability that the person is 0-14 years old, given that the person is female.

Algebra
ProbabilityFind the probability. Express the result as a reduced fraction and a decimal rounded to the nearest thousandth.
Dry erase markers. Suppose 6 markers in a box of two dozen are out of ink (dry). If an instructor selects 1
marker and then another at random from the box without replacement, find the probability that he chooses 2 dry markers.

Math
ProbabilityConsider two electrical components, A and B, with
respective lifetimes X and Y in days. Assume that a joint
PDF of X and Y is
If 0<x< 1 and 0 <y < 2, and 0 otherwise, find:
a. the marginal density of X
b. the marginal density of Y

Math
ProbabilityATV remote control has keys for channels 0 through 9.
a) If a key is selected at random, what is the probability that the key for channel 8 is pressed?
b) If a key is selected at random, what is the probability that the key for an even number is pressed?
c) If a key is selected at random, what is the probability that the key for a number more than 0 is pressed?

Math
ProbabilityThe theoretical probability of a coin landing heads up is Does this probability mean that if a coin is flipped two times, one flip will land heads up? If not, what does it mean?
Choose the correct answer below.
A. No, it means that if a coin was flipped many times, at most 1/2 of the tosses would land heads up.
B. Yes, it means that if a coin was flipped two times, at least one of the tosses would land heads up.
C. No, it means that if a coin was flipped many times, about 1/2 of the tosses would lands heads up.
D. Yes, it means that if a coin was flipped two times, exactly one of the tosses would land heads up.

Math
ProbabilitySuppose the random variable is best described by a normal distribution with μ = 20 and a = 8.2. Find the z-score that corresponds to each of the following a values.
Express your answers rounded correctly to the hundredths place.
(a) x = 15
z=
(b) x = 32
z=
(c) x= 10
z=
(d) x = 25
z=
(e) x= 25
z=
(f) x=17
z=

Math
ProbabilityA spinner has an equal chance of landing on each of its five numbered regions. You spin twice. The first spin lands in region two and the second spin lands in region one.
21/55≈ 0.382
1/25≈0.04
1/4≈0.25
4/15≈0.267
7/22≈0.318

Math
ProbabilitySuppose a simple random sample of size n = 11 is obtained from a population with μ-66 and o=14
(a) What must be true regarding the distribution of the population in order to use the normal model to compute probabilities regarding the sample mean? As
the normal model can be used, describe the sampling distribution x.
(b) Assuming the normal model can be used, determine P(x <69.3).
(c) Assuming the normal model can be used, determine P(x ≥ 67.9).
(a) What must be true regarding the distribution of the population?
A. The population must be normally distributed.
B. There are no requirements on the shape of the distribution of the population
C. The population must be normally distributed and the sample size must be large
D. Since the sample size is large enough, the population distribution does not need to be normal.

Math
ProbabilityIn a survey, it was found that 78% of the population of a certain urban area lived in single-family dwellings and 22% in multiple housing. Five years later, of those who had been living in single-family dwellings, 91% still did so, but 9% had moved to multiple-family dwellings. Of those in multiple housing, 96% were still living in that type of housing, while 4% had moved to single-family housing. Assume that these trends continue. Answer parts (a) through (f).

Math
ProbabilityAt one liberal arts college, students are classified as humanities majors, science majors, or undecided. The chances are 10% that a humanities major will change to a
science major from one year to the next, and 45% that a humanities major will change to undecided. A science major will change to humanities with probability 0.25,
and to undecided with probability 0.25. An undecided will switch to humanities or science with ptobabilities of 0.30 and 0.40, respectively. Complete parts (a) and (b)
below.
(a) Find the long-range prediction for the fraction of students in each of these three majors.
First, find the transition matrix P. Let the first state be that a student is a humanities major, the second that a student is a science major, and the third state that a
student is undecided.

Math
ProbabilityPrevious question
In a survey, it was found that 78% of the population of a certain urban area lived in single-family dwellings and 22% in multiple housing. Five years later, of those who
had been living in single-family dwellings, 91% still did so, but 9% had moved to multiple-family dwellings. Of those in multiple housing, 96% were still living in that type
of housing, while 4% had moved to single-family housing. Assume that these trends continue. Answer parts (a) through (f).
Type an integer vi matavimax Cicht.)
(c) What percent of the population can be expected in each category after 5 years?
The percent of the population in single-family housing is %.
The percent of the population in multiple housing is.
(Round to one decimal place as needed.)
(d) What percent of the population can be expected in each category after 10 years?
The percent of the population in single-family housing is %.
The percent of the population in multiple housing is %.
(Round to one decimal place as needed.)
(e) Find the transition matrix for a 10-year period.
sinale multiple
point possible
- Wol

Math
ProbabilityA class has 20 students. What is the probability that at least 5 students were born on a weekend?
82%
1.4%
45%
72%
20 pts

Math
ProbabilityA basketball player has a 62% chance of making each free throw. What is the probability that the player makes exactly four out of six free throws?
66%
1.86%
22%
32%

Math
ProbabilityA customer can pick a meat, a vegetable, and a potato for a meal at a restaurant. The choices for each are listed below.
Meat: fish, chicken, or beef
Vegetable: broccoli or corn
Potato: mashed or baked
How many different meals can be chosen?

Math
ProbabilityA game costs $1 to play where you win $5 when a coin lands on heads but lose $6 when a coin lands on tails. Calculate the expected payoff to the nearest cent, being sure to show all work.
![Suppose that 15% of surveyed kids say that chocolate is their favourite food to eat. If 40 kids are asked what their favourite food is, what is the probability that between 80-85% (inclusive) of them, will say something other than
chocolate? [4]](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/77152293-1660226561.973818.jpeg?w=256)
Math
ProbabilitySuppose that 15% of surveyed kids say that chocolate is their favourite food to eat. If 40 kids are asked what their favourite food is, what is the probability that between 80-85% (inclusive) of them, will say something other than
chocolate? [4]
![In a manufacturing process of Headache medicine (pills), the company is aware of a defect rate of 0.02%. Given that this defect is in the shape only of the pill (not the medicinal ingredients) they are okay with this defect rate
and decide to continue production. If a small pharmaceutical company decides to purchase 1000 pills...
a. Find the probability that at least 1 is defective. [2]
b. Find the probability that no more than 2 are defective [3]
c. What is the expected number of defective pills in this purchase? [1]](https://media.kunduz.com/media/sug-question/raw/77151839-1660222974.66817.jpeg?w=256)
Math
ProbabilityIn a manufacturing process of Headache medicine (pills), the company is aware of a defect rate of 0.02%. Given that this defect is in the shape only of the pill (not the medicinal ingredients) they are okay with this defect rate
and decide to continue production. If a small pharmaceutical company decides to purchase 1000 pills...
a. Find the probability that at least 1 is defective. [2]
b. Find the probability that no more than 2 are defective [3]
c. What is the expected number of defective pills in this purchase? [1]

Math
Probability8. Which of these discrete variables has a binomial distribution?
a. The number of diamonds dealt from a deck of cards
b.The number of men selected in a 5-member committee from Q6.
c. The number of Os produced by a random-number generator
d. None of the above

Math
ProbabilityWhich of the following is an example of a uniform distribution?
a. Length of time you play in a baseball game
b.A coin toss 8 times, probability you get heads
c.A random number generator
d. The number of votes in an election for a particular party

Math
ProbabilityA study of 468 randomly selected kindergarten students showed that they have seen on average 5723 hours of television. If the sample standard deviation of the population is 951, find the upper bound limit of the 95% confidence interval of the mean for all students.

Math
ProbabilitySuppose that a card is drawn from a well-shuffled deck of 52 cards. What is the probability of drawing each of the following?
a) A queen
b) An ace or a 9
c) A club
d) A red queen
a) What is the probability of drawing a queen?
(Simplify your answer. Type an integer or a fraction.)
b) What is the probability of drawing an ace or a 9?
(Simplify your answer. Type an integer or a fraction.)
c) What is the probability of drawing a club?
(Simplify your answer. Type an integer or a fraction.)
d) What is the probability of drawing a red queen?
(Simplify your answer. Type an integer or a fraction.)

Math
ProbabilityFind the probability. There are twelve shirts in your closet, six blue and six green. Two of the blue shirts and two of the green shirts fit well. The others are too big. You randomly select a shirt to wear. It is blue or is too big.
6/11≈ 0.545
10/11≈ 0.909
7/8=0.875
5/6≈ 0.833
8/11≈ 0.727

Math
ProbabilityResidents of a gated community use a five-digit code to open the gate. What is the probability that a robber will enter the code correctly on a first random try? Assume the code allows repeated digits.
0.00001
0.0001
0.001
0.01

Math
ProbabilityOn an assignment, there are two true or false questions. You have no idea what the correct answer is to either one so you guess.
a. What is the probability that you get both of them right by guessing? Explain your answer.
b. What is the probability that you get exactly one of them right by guessing?
Explain your answer.
Write your answers as fractions.
a. The probability that you get both of them right is
b. The probability that you get exactly one of them is right

Math
ProbabilityThere are five different fish, each of a different species, in a tank that needs to be cleaned. What is the probability that
the first two scooped out are a goldfish and a guppy, in that order, assuming both are included among the species in the
tank?
1/20
1/60
1/12
1/30

Math
ProbabilityA marble is drawn from a box containing 3 yellow, 2 white, and 14 blue marbles. Find the odds in favor of drawing the following.
(a) A yellow marble
(b) A blue marble
(c) A white marble
(a) In reduced form, the odds in favor of drawing a yellow marble are __ to __
(Simplify your answers.)
(b) In reduced form, the odds in favor of drawing a blue marble are __ to __ .
(Simplify your answers.)
(c) In reduced form, the odds in favor of drawing a white marble are __ to __
(Simplify your answers.)

Math
ProbabilityOne bag contains three white marbles and five black marbles, and a second bag contains four white marbles and six black marbles. A person draws one marble from each bag. Find the probability that both marbles are black.
55/91
25/72
3/8

Math
ProbabilityThe amount of time to complete a physical activity
in a PE class is normally distributed with a mean of
39.8 seconds and a standard deviation of 6.3
seconds. Round answers to 4 decimal places.
a) What is the probability that a randomly chosen
student completes the activity in less than 32.3
seconds?
b) What is the probability that a randomly chosen
student completes the activity in more than 45.3
seconds?
c) What proportion of students take between 34.6
and 44.9 seconds to complete the activity?
d) 80% of all students finish the activity in less than
seconds.

Math
ProbabilityWhich of the following statements is true?
"Unusual" values of z are those such that |z| < 1
If the confidence level increases then the critical values will move away from 0.
If the number of items in a sample is increased, then the margin of error computed within a confidence interval will also increase.
A 95% confidence interval for the population mean can be interpreted to say that the population mean has a 95% chance of falling within the limits of the
confidence interval

Math
ProbabilityA restaurant packed lunches for an event. Each lunch had a sandwich, a side, and a cookie.
•Sandwich choices: ham, turkey, cheese
• Sides: chips, apple, carrot sticks, celery, orange
• Cookie choices: chocolate chip, oatmeal, sugar, snickerdoodle
Assuming the probabilities of each selection are the same for all options in a category, what is the probability of randomly choosing a lunch containing a cheese sandwich, chips, and a chocolate chip cookie?
1/60
60
1/1.320
1,320

Math
ProbabilityThis question: 3 point(s) possible
A single die is rolled twice. The set of 36 equally likely outcomes is ((1.1), (1,2), (1,3), (1,4), (1,5), (1,6), (2,1), (2,2), (2,3), (2,4), (2,5), (2,6), (3,1), (3,2), (3,3), (3,4), (3,5), (3,6), (4,1), (4,2), (4,3), (4,4), (4,5), (4,6), (5,1), (5,2), (5,3), (5,4).
(5,5), (5,6), (6,1), (6,2), (6,3), (6,4), (6,5), (6,6)). Find the probability of getting two numbers whose sum is less than 13.